Depending on who you talk to, 5G is either ushering in a new decade of connectivity and enhanced opportunity or is over-hyped and potentially harmful. Whichever side of the fence you’re on, there’s no doubt that the telecommunications industry is going through a pivotal change. Momentum is building as telecoms providers around the world rollout 5G, accompanied by a deluge of marketing campaigns and the usual concerns that surround new technology.
Here we’ll help you to cut through the smoke and mirrors so that you can come to your own informed conclusion.

What is 5G and How Did We Get Here?
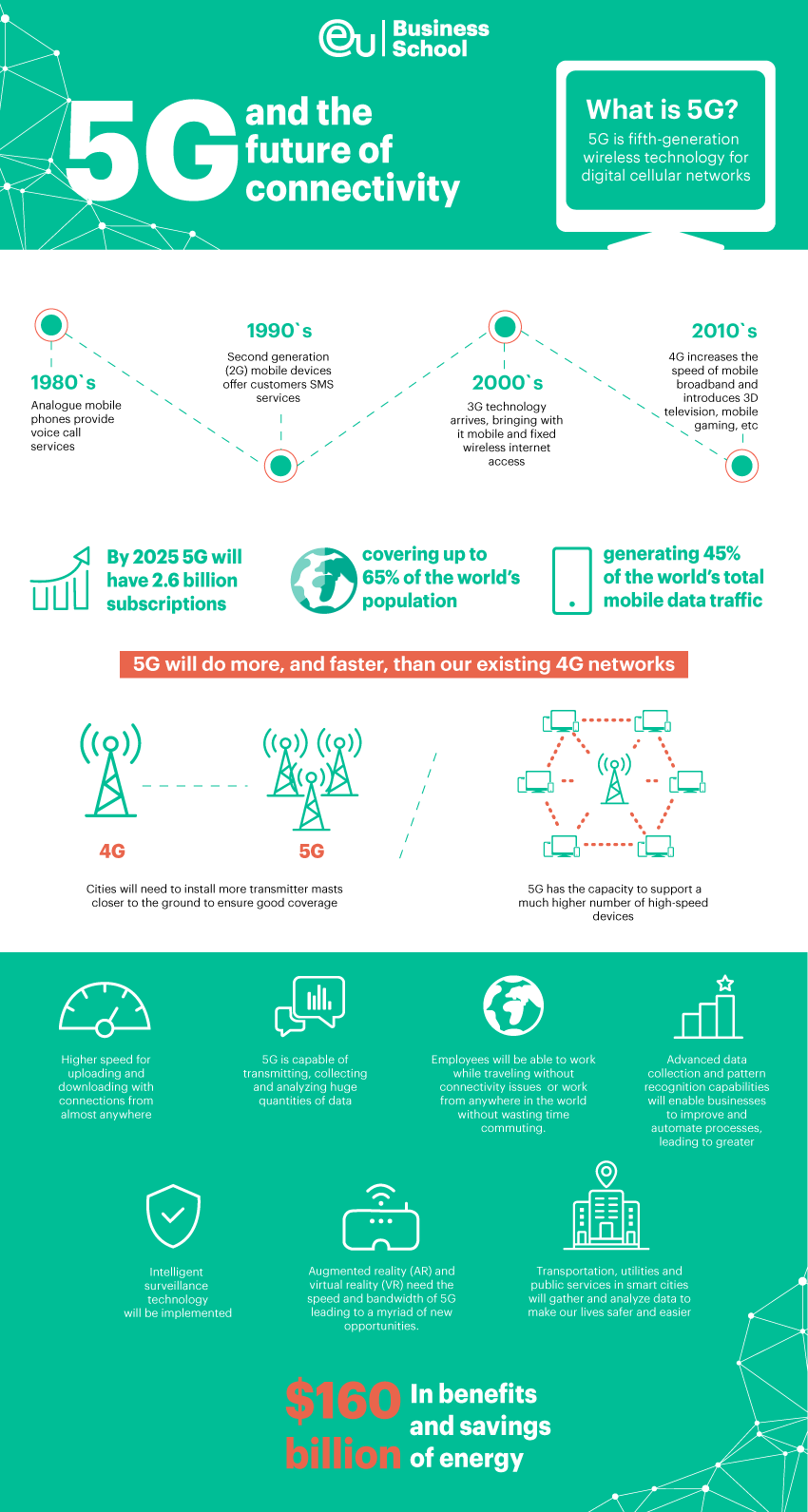
So, what is 5G? The ‘G’ stands for generation; 5G is fifth-generation wireless technology for digital cellular networks. It’s helpful to understand 5G in the context of the developments that have taken place roughly every ten years since the 1980s.
1980s – Analogue mobile phones provide voice call services only to their initially limited audience.
1990s – Devices move from analogue to digital; second generation (2G) mobile devices offer customers SMS services which rapidly became the leading method of communication around the world.
2000s – 3G technology arrives, bringing with it mobile and fixed wireless internet access, video calls, and mobile TV, giving us all connectivity on the go.
2010s – 4G increases the speed of mobile broadband and introduces 3D television, mobile gaming, high-definition mobile TV and video conferencing.
Which brings us to today; 5G networks are operating in cities around the world and 5G-enabled devices have already been released, but whether you can take advantage of the benefits of 5G yet will depend on where you are based and the provider that you are with, as each company has a different plan for rolling out the service. The Ericsson Mobility Report forecasts that by 2025 5G will have 2.6 billion subscriptions covering up to 65% of the world’s population and generating 45% of the world’s total mobile data traffic, making it the fastest developing mobile communication technology to have ever been rolled out on a global scale. That’s possible, at least in part, to the way that 5G works.
How Does 5G Work and Is It Harmful?
5G builds upon existing infrastructure to provide super-fast connections with low latency and high connection density.
Low latency is a term used to describe a network that is optimized to process a very high volume of data messages with minimal delay. Connection density describes the ability to support the successful delivery of a message of a certain size within a certain time. Which essentially means that 5G will do more, and faster, than our existing 4G networks.
Just like TVs, radios and our existing mobile devices, 5G relies on the electromagnetic spectrum to work, and will produce electromagnetic radiation. However, long term studies have not revealed any health implications from exposure to this level of radiation.
The 5G spectrum, as permitted under international guidelines, sits across non-ionizing radio waves, which physicist and cancer researcher David Grimes defines as “lack[ing] sufficient energy to break apart DNA and cause cellular damage”, and microwaves, which Professor Rodney Croft, adviser to the ICNIRP, notes are at such low levels that heating effects are not harmful.
5G waves are only able to travel a short distance. That means we will need to place more transmitter masts closer to the ground to ensure good coverage. However, each of these will run on lower power than current masts, meaning that we will actually be exposed to lower levels of electromagnetic radiation than we are now.
What Changes Will I Notice?
In the short-term you are not likely to notice any great changes. 5G is not replacing 4G so, whilst you need a 5G-enabled device to access the new network, you will still be able to use your 4G devices. You may even see a faster connection as more people migrate to 5G networks, increasing capacity and therefore speed for 4G users.
If you decide to move to a 5G-enabled device, you will have access to a similar offering to 4G devices but with a much smoother experience. A better connection on 5G will mean video calls don’t stutter and location responsive apps don’t freeze. Real-time video conferencing will become a more reliable option for businesses. The gamers experience will also improve, particularly between international players. This could have interesting benefits in the corporate setting, for example enabling internationally based colleagues to take part in real-time team-building activities together.
Foldable phones and smart glasses require the capabilities of 5G to live up to their full potential. If you are considering investing, make sure your new device is 5G-enabled and that your provider offers 5G access. You may also notice aesthetic changes to wearable devices as 5G’s lower power requirements will allow for slimmer batteries.
Lastly, if you have ever tried to use Wi-Fi across multiple devices in a crowd (at conferences, for example), you’ll be pleased to know that inevitably slow and frustrating experience will become a thing of the past. 5G has the capacity to support a much higher number of devices at high speed, so we won’t need to stress about downloads, uploads and video calls in public places anymore.
What Challenges Will 5G Cause?
Change is never without challenge and, as we get closer to universal adoption of 5G, we should be aware of the potential challenges that lie ahead.
Businesses embracing 5G should consider their data strategy. 5G will bring an avalanche of data and, as a recent survey by Ensighten found, 65% of marketing professionals are already overwhelmed by the amount of data they have whilst 85% are not able to fully utilize existing data. 5G is capable of transmitting, collecting and analyzing huge quantities of data; chief technology officers should have clear strategies outlining what they will collect and store, and how they will use the information to achieve business goals.
Concern has also been raised about how 5G could exacerbate the existing digital divide. The rollout will prioritize geographic areas of high use and profitability, meaning that remote and underdeveloped places around the world will initially be at a disadvantage when it comes to access. However, following the rollout this trend could be reversed. The Brookings Institution reported that in America 35% of Hispanics and 24% of African Americans ‘have no other online connection except through their smartphones or other mobile devices’. 5G will offer the same experience to those with and without a wired connection, which could level the playing field if a fair pricing system is adopted by providers around the world.
What New Business Opportunities Will 5G Bring?
The new network will provide myriad opportunities for businesses to save time and money.
Improving Productivity
5G devices will have ultra-fast capabilities built into them. Once the rollout is complete, it will be possible to connect from virtually anywhere. Freelancers will no longer need to rely on the strength of local Wi-Fi signals. Employees will be able to work whilst travelling without attendant connectivity issues, or work from anywhere without wasting time commuting. Waiting time for uploads and downloads will also be drastically reduced.
Advanced data collection and pattern recognition capabilities will enable businesses to improve and automate processes, leading to greater efficiency and safety. This will allow human intelligence to be directed to where it’s really needed.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) need the speed and bandwidth of 5G. Once it’s been rolled out, complex, real-time remote and virtual work will become a reality, with positive implications anticipated across industry. One possible scenario is a building inspector leaving bulky plans behind and using smart glasses to see a building’s electrics layered over the walls. AR used in this way will lead to greater professional efficiency and effectiveness.


Transforming Industry
The manufacturing industry is set to benefit significantly from the move to 5G. Factory automation, assembly line maintenance, remote production inspection and a move away from wired connections for networked machinery will save time and money for global businesses who are ready and able to invest.
The energy sector will also be transformed by the introduction of remote transmission tower monitoring and the ability to connect previously hard-to-reach infrastructure, such as oil rigs and electricity substations, that historically have not been connected.
Communications
Proximity-targeted marketing enables companies to reach customers with location-specific advertising. The technology is already available but is plagued by hackers using GPS spoofing. However, 5G’s reliance on microcells offers a secondary means of verification, which will make this a more reliable and fruitful marketing tool.
How Will 5G Transform Cities?
There are many socially beneficial use cases for 5G which predict a future where the robots look after us, rather than something more dystopian.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will rely heavily on 5G. Although there are many applications for this technology, it will most immediately appear in intelligent surveillance technology and driverless cars. Both require high-speed connections to transmit and instantly analyze large quantities of data.
AR and VR could be used across public service provision and training. Firefighters, for example, could receive plans for burning buildings through AR headsets, making rescue operations safer and faster. Remote patient-monitoring and telesurgery will improve as the lag in real-time connections is eliminated, increasing access to expertise for poorer people and for those living in remote or dangerous places.
5G-enabled technology is also forecast to save vast sums of public money. According to a white paper from Accenture, reductions in energy usage, traffic congestion and fuel costs alone could produce over $160 billion in savings.
These examples fall into the broader category of Smart Cities, where transportation, utilities and public services will gather and analyze data to make our lives safer and easier.
Who Is Leading the Way?
The rollout of 5G technology began in 2019, with providers around the world announcing comprehensive strategies to bring the new network to their commercial and personal customers. 5G is already available in some cities, but it will be some time before the rollout is complete. The first phase – already in play – will give anyone with a 5G-enabled device access to enhanced mobile broadband, delivering a faster and more reliable mobile connection. The second phase will bring in the kinds of connections that will be used for driverless cars and smart cities.


Amongst many active players Ericsson is leading the way. They are the first provider to have established live 5G networks on four continents and are driving standardization of the technology, partnering with leading telecoms companies around the world to create a cross-industry ecosystem of expertise. At last year’s Mobile World Congress Fredrik Jejiling, Head of Networks at Ericsson, commented “who could have thought we’d get Uber out of 4G? With great technology in the hands of [innovative people], magical things can happen”.
Preparing for the Future of Connectivity
As 5G is adopted by individuals and businesses around the world, groundbreaking uses for the technology will emerge that no one has yet been able to imagine. In order to prepare for the potential of tomorrow, it is essential to understand the nature of business today.
At EU Business School, our experiential approach to learning immerses students in the world of business through visits to leading global companies, putting theory into practice whilst gaining industry insights, learning from leaders, entrepreneurs and visionary business professionals through talks and workshops to find out what it takes to get ahead, succeed and adapt in the dynamic global market.
If you’re interested in an education that’ll put you at the forefront of emerging technologies, trends and insights, with a solid theoretical and pragmatic foundation, EU is the school of choice for you.